
Thin, lateral bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow.Ankle Joint: Anatomy as part of the ankle It articulates with the tibia and fibula to form the ankle joint. Articulates with the talus Talus The second largest of the tarsal bones.
 Distal projection Projection A defense mechanism, operating unconsciously, whereby that which is emotionally unacceptable in the self is rejected and attributed (projected) to others. Medial malleolus Medial malleolus Ankle Joint: Anatomy :. Shaft: anterior, lateral, and posterior surfaces. Site of attachment Attachment The binding of virus particles to virus receptors on the host cell surface, facilitating virus entry into the cell. Triangular, superior–anterior area where condyles merge. Separated by the lateral and medial intercondylar tubercles. Horizontal proximal surfaces that articulate with the femoral condyles. Articulates with the femur and fibula proximally and the talus Talus The second largest of the tarsal bones. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Medial, weight-bearing bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Foot: Anatomy, and toes.īones and Joints Tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. The bones of the foot form longitudinal and transverse arches and are supported by various muscles, ligaments, and tendons. The foot comprises 26 bones, including the tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges. Cellulitis and exert their action on the ankle, foot Foot The foot is the terminal portion of the lower limb, whose primary function is to bear weight and facilitate locomotion. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. The muscles of the leg are grouped into the anterior, lateral, and posterior compartments by extensions of fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. Knee Joint: Anatomy and fibula bones, which articulate with each other at the proximal and distal tibiofibular Distal tibiofibular Ankle Joint: Anatomy joints. The bony structure is composed of the tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. The ankle primarily allows plantar flexion and dorsiflexion of the foot. The lower leg, or just “leg” in anatomical terms, is the part of the lower limb between the knee and the ankle joint Ankle joint The ankle is a hinged synovial joint formed between the articular surfaces of the distal tibia, distal fibula, and talus. Students: Educators’ Pro Tips for Tough Topics. Fundamentals of Nursing: Clinical Skills.
Distal projection Projection A defense mechanism, operating unconsciously, whereby that which is emotionally unacceptable in the self is rejected and attributed (projected) to others. Medial malleolus Medial malleolus Ankle Joint: Anatomy :. Shaft: anterior, lateral, and posterior surfaces. Site of attachment Attachment The binding of virus particles to virus receptors on the host cell surface, facilitating virus entry into the cell. Triangular, superior–anterior area where condyles merge. Separated by the lateral and medial intercondylar tubercles. Horizontal proximal surfaces that articulate with the femoral condyles. Articulates with the femur and fibula proximally and the talus Talus The second largest of the tarsal bones. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Medial, weight-bearing bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Foot: Anatomy, and toes.īones and Joints Tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. The bones of the foot form longitudinal and transverse arches and are supported by various muscles, ligaments, and tendons. The foot comprises 26 bones, including the tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges. Cellulitis and exert their action on the ankle, foot Foot The foot is the terminal portion of the lower limb, whose primary function is to bear weight and facilitate locomotion. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. The muscles of the leg are grouped into the anterior, lateral, and posterior compartments by extensions of fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. Knee Joint: Anatomy and fibula bones, which articulate with each other at the proximal and distal tibiofibular Distal tibiofibular Ankle Joint: Anatomy joints. The bony structure is composed of the tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. The ankle primarily allows plantar flexion and dorsiflexion of the foot. The lower leg, or just “leg” in anatomical terms, is the part of the lower limb between the knee and the ankle joint Ankle joint The ankle is a hinged synovial joint formed between the articular surfaces of the distal tibia, distal fibula, and talus. Students: Educators’ Pro Tips for Tough Topics. Fundamentals of Nursing: Clinical Skills. 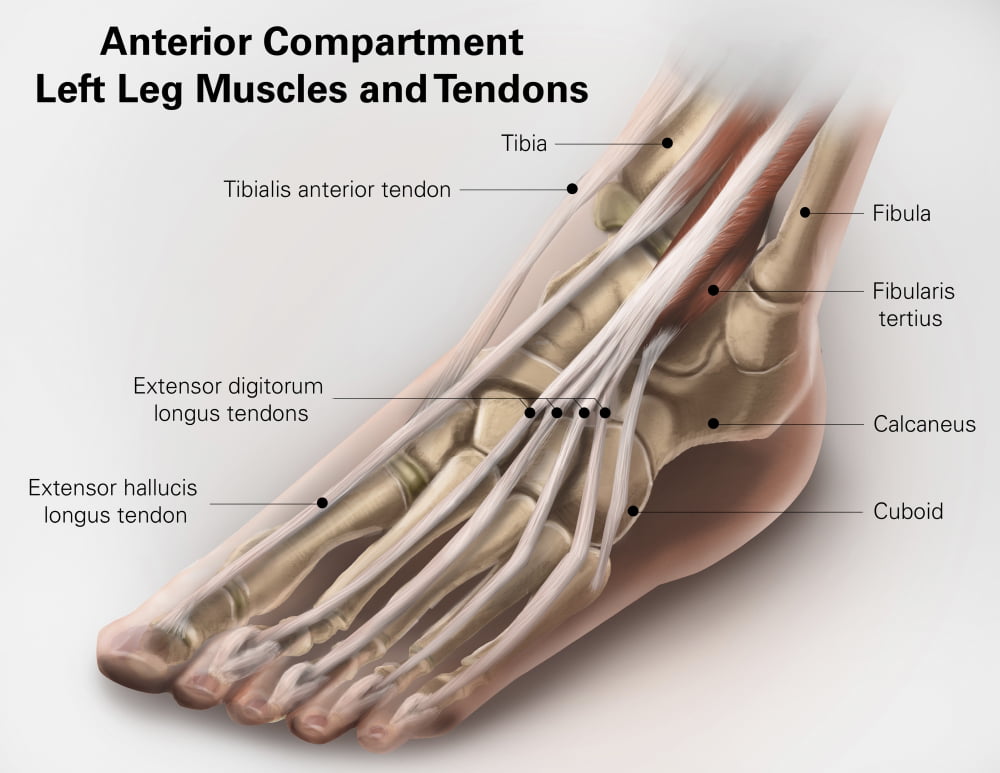
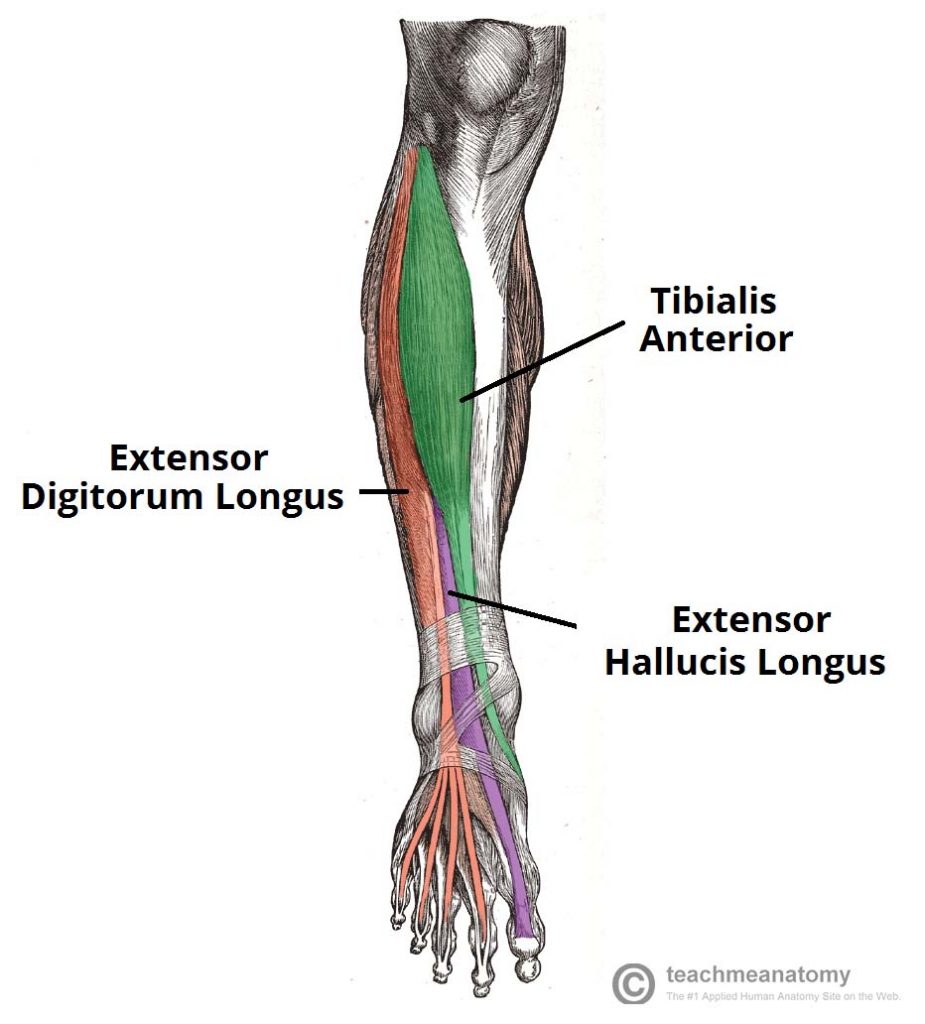
Semitendinosus – supplied by tibial part of sciatic nerveĮnumerate the muscles responsible for dorsiflexion and inversion of foot.Įnumerate the structures passing deep to superior extensor retinaculum from medial to lateral.Lower 1/4 th of the medial surface of fibula.ĭorsal surface of base of fifth metatarsal.Įnumerate the muscles inserted on the upper part of the medial surface of tibia and their nerve supply. Upper1/4 th and anterior half of middle 2/4 th of the medial surface of fibula and adjacent interosseous membrane.īase of middle and distal phalanx of lateral four toes through extensor expansion. Posterior half of middle 2/4 th of the medial surface of fibula and adjacent interosseous membrane. Maintains medial longitudinal arch of foot Inversion of foot at subtalar and midtarsal joints.
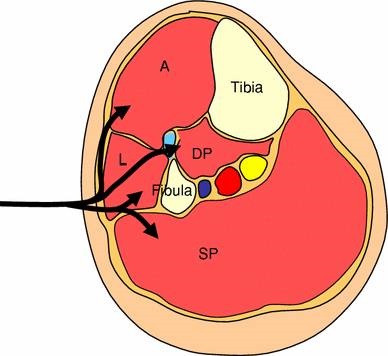
Upper 2/3 rd of lateral surface of tibia and adjoining part of interosseous membrane. Write the origin, insertion and action of muscles of anterior compartment of leg. * All the muscles of the anterior compartment of leg are supplied by deep peroneal nerve.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
